- Research & Education
- Trading
mt5 platforms
Trading Products
ACCOUNT TYPES

- Partnership
- About us
- Contact us
An index is a basket of selected stocks that represent a particular market, sector, or asset class. It serves as a benchmark to measure the performance of a group of stocks.
Trading indices involves speculating on the overall performance of the stocks within the index rather than trading individual stocks. Traders can go long (buy) if they expect the index to rise or go short (sell) if they anticipate a decline.
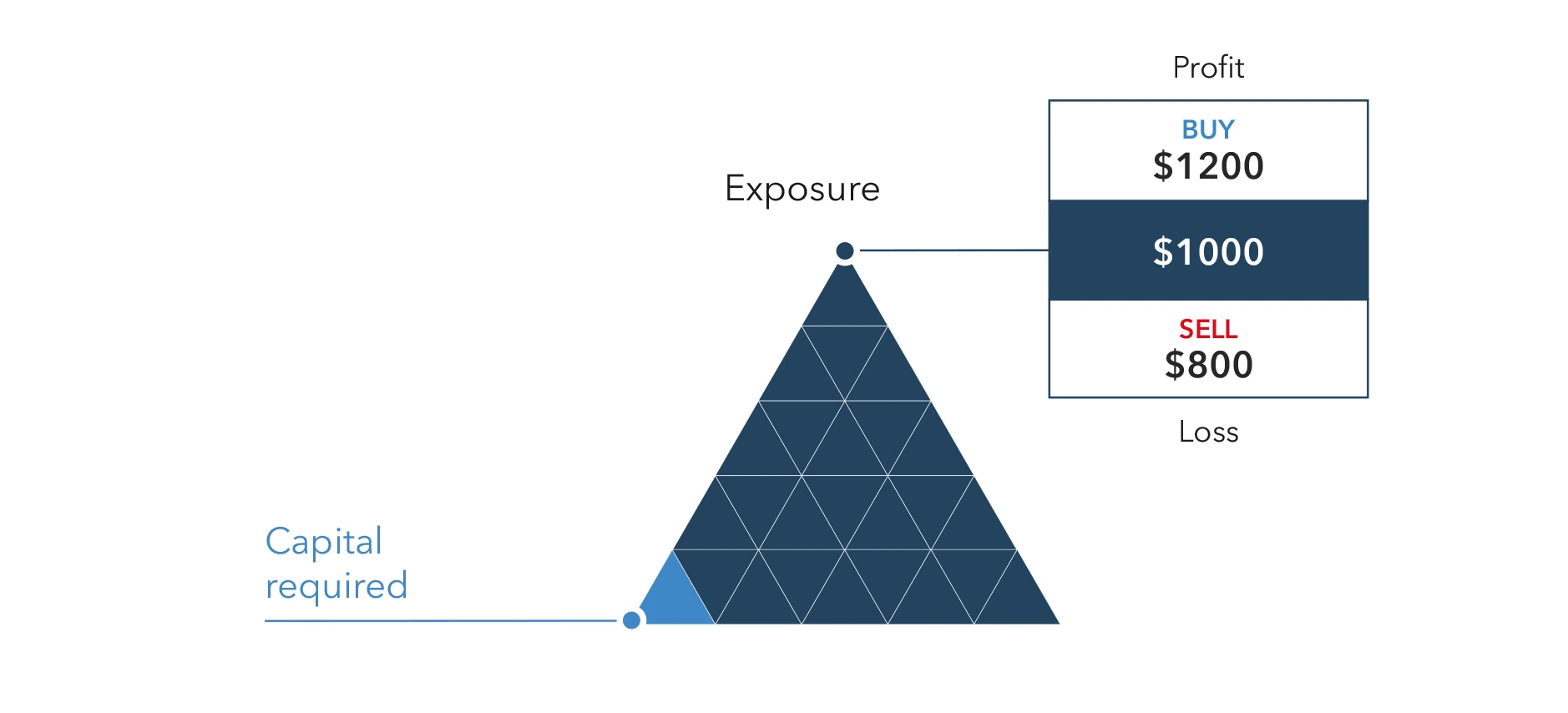
Indices offer diversification benefits as they include a range of stocks from different companies. This diversification helps spread risk and reduces exposure to the performance of individual stocks.
Some well-known indices include the S&P 500 (US), Dow Jones Industrial Average (US), FTSE 100 (UK), DAX 30 (Germany), Nikkei 225 (Japan), and many others covering various regions and sectors.
Traders can access index trading through various financial instruments, including
Futures contracts based on the value of the underlying index. They allow traders to speculate on the future value of the index.
Options contracts based on the underlying index, offering the right but not the obligation to buy or sell at a specified price.
Commodity ETFs are investment funds that track the price movements of specific commodities or commodity indices. They are traded on stock exchanges like regular stocks. Investing in commodity ETFs allows investors to gain exposure to commodity markets without directly holding futures contracts or physical commodities.
Contracts for Difference (CFDs) allow traders to speculate on index price movements without owning the underlying asset.
Index movements are influenced by a combination of factors, including economic indicators, corporate earnings, geopolitical events, and market sentiment.
Major indices are highly liquid, meaning they have a high volume of trading activity, making it easy to enter or exit positions.
Trading indices carries risks, including market volatility, sudden price fluctuations, and potential losses from leverage if using leveraged products like index futures or CFDs.
Traders use various strategies, including technical analysis, fundamental analysis, and algorithmic trading, to identify potential entry and exit points.
Index trading appeals to both short-term traders and long-term investors seeking exposure to broader market movements or specific sectors.